RAID Overview
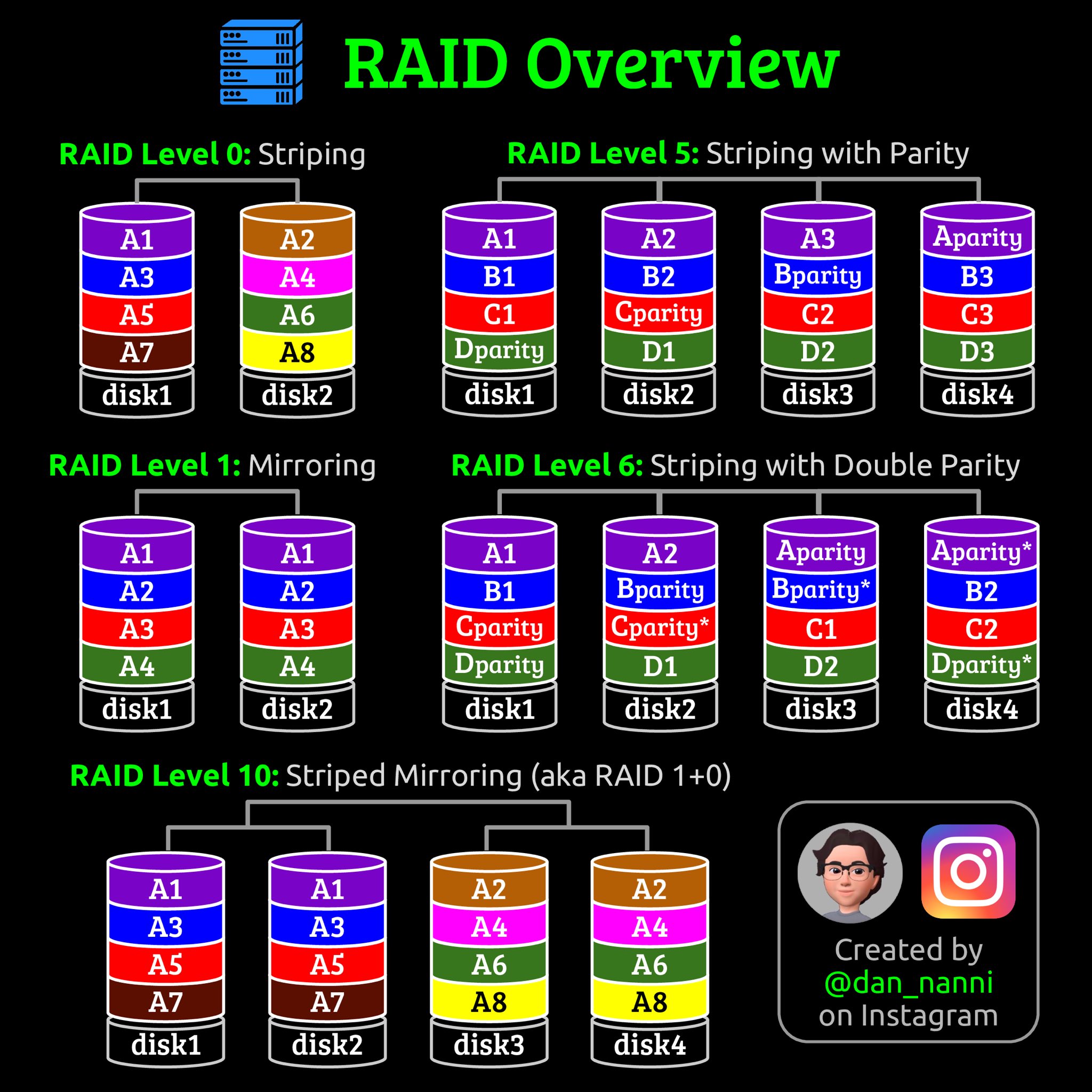
- RAID 0: It is called striping, which allows you to split the data into multiple disks without redundancy.
- RAID 1: It is called mirroring, which allows you to create a complete copy of data on multiple disks.
- RAID 5: It distributes the parity information and data on multiple disks.
- RAID 6: It is the improved version of RAID 5 as it uses two sets of parity information to provide higher data redundancy.
- RAID 10: It combines RAID 0 and RAID 1 to generate the set of mirror disks to improve performance and redundancy.
Assume that you have a mixed configuration comprising disks organized as RAID 1 and RAID 5 disks. Assume that the system has flexibility in deciding which disk organization to use for storing a particular file. Which files should be stored in the RAID 1 disks and which in the RAID 5 disks in order to optimize performance?
RAID 1(Mirroring)
- RAID 1 provides redundancy by mirroring data across multiple disks. Every write operation is duplicated on both disks in the mirrored pair
- It offers high read performance as data can be read form either disk in the mirror pair.
- Files that require high read performance and are critical in terms of availability or reliability should be stored in RAID 1. This includes system fiels, frequently accessed application binaries, and critical DB files.
RAID 5(Striping with Parity)
- RAID 5 offers a balance between performance, redundancy, and usable storage capacity. It uses block-level striping with distributed parity across multiple disks.
- Read performance is generally good, especially for large sequential reads, as data can be read in parallel from multiple disks.
- Write performance can be slower than RAID 1, particularly for small random writes, due to the need to calculate parity infromation.
Based on these consideration:
- Critical system files, frequently accessed application binaries, and important database file should be sotred on RAID 1 disks to ensure high read performance and redundancy.
- User files, documents, media files, and less critical application data can be stored on RAID 5 disks to make efficient use of storage capacity while still providing redundancy and acceptable performance.