This post was written for
studying. There maybe a lot wrong going on.
목차
How does the traceroute work?
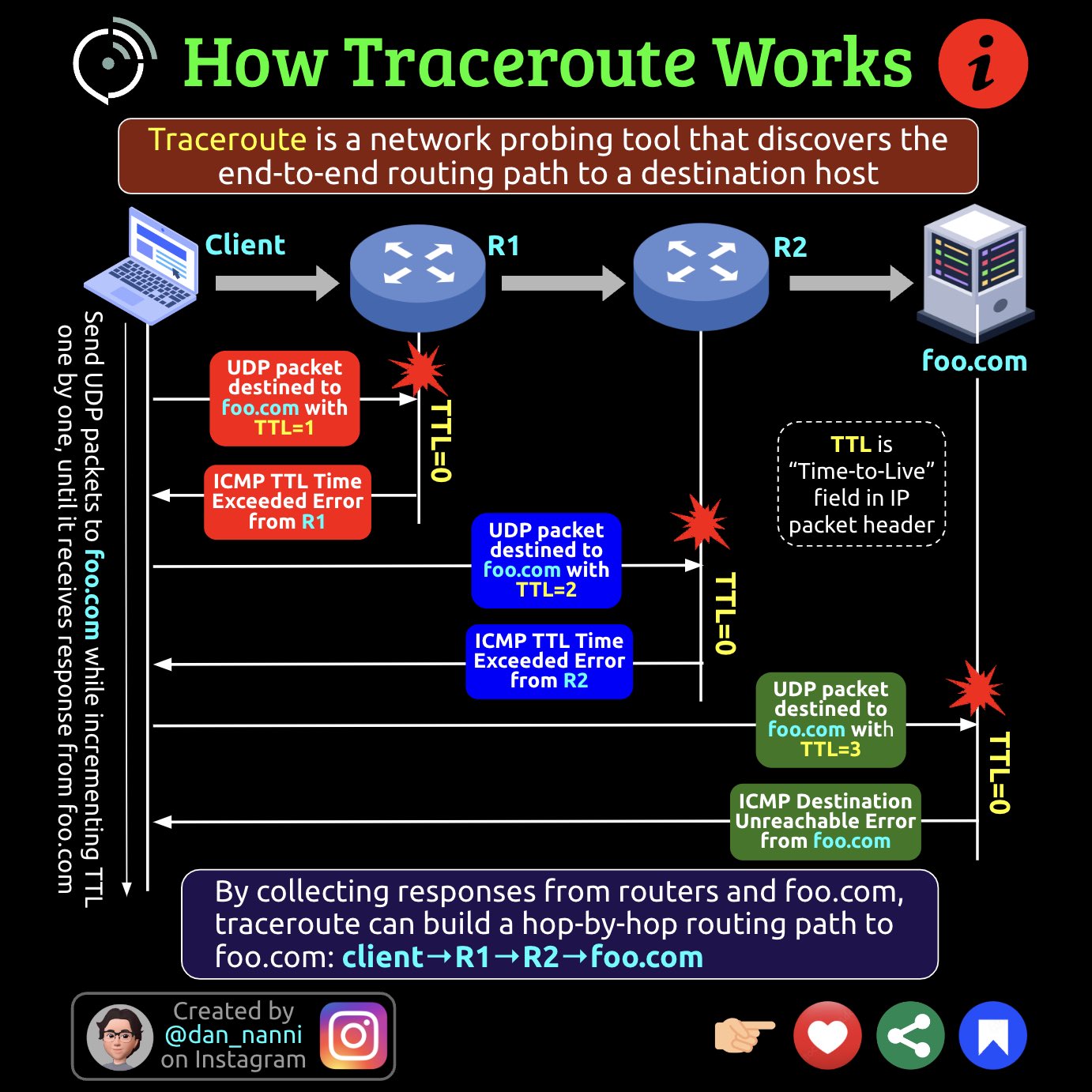
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to trace the route that packets take from one host to another across a network. It works by sending a series of packets, each with an increasing Time to Live (TTL) value, towards the destination host. Here’s how traceroute works step by step:
-
Initial Packet: The traceroute tool sends the first packet with a TTL value of 1 to the destination host. The TTL value indicates the maximum number of hops (routers) that the packet can pass through before being discarded.
-
First Hop: The packet travels from the sender’s host to the first router (hop) in the network path towards the destination. Since the TTL value is 1, the packet expires upon reaching this router, and the router sends back an ICMP Time Exceeded message to the sender.
-
Receiving ICMP Response: The sender’s host receives the ICMP Time Exceeded message from the first router, indicating that the TTL expired. Traceroute records the IP address of the first router and calculates the round-trip time (RTT) for the packet’s journey to and from the router.
-
Incrementing TTL: Traceroute repeats the process, sending another packet with a TTL value of 2. This causes the packet to travel to the second router in the network path before expiring and triggering an ICMP Time Exceeded message.
-
Recording Hops: As the process continues, traceroute records the IP addresses of each router (hop) along the path to the destination, along with the corresponding RTT for each hop.
-
Completing the Trace: Traceroute continues sending packets with increasing TTL values until it reaches the destination host. Once the destination host receives the packet, it sends back an ICMP Echo Reply message to the sender, indicating that the destination has been reached.
-
Displaying Results: Traceroute presents the recorded information to the user, showing the IP addresses of the routers traversed, along with the RTT for each hop.
domicmeia@domicmeia:~$ traceroute google.com
traceroute to google.com (142.250.66.142), 30 hops max, 60 byte packet
It doesn’t work..
Windows tracert sends only ICMP packets, while UNIX/Linux traceroute sends UDP datagrams by default, but can also send TCP segments. Because many routers block ICMP packets, if traceroute fails from a Windows system, running it on a Linux or UNIX system may return more complete results. The reverse is true as well. Routers could be blocking UDP (many in fact do block UDP-based trace-routes), and then the ICMP version becomes the more informative one.